Projekte
» Dysphagie
Schluckstörungen und nachfolgende Lungenentzündung sind einer der häufigsten Todesursachen nach Schlaganfall. Mit der geplanten Studie sollen Reorganisation und Restitution nach neurogener Dysphagie untersucht werden. Ausserdem soll die unterschiedliche cerebrale Repräsentation verschiedener Schluckphasen bei Gesunden (junge und ältere Probanden) differenziert werden.
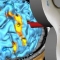
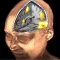
Oben: Darstellung einer Hirnstammläsion mit daraus folgender Dysphagie und Diffusionstraktografie der durchgehenden Bahnsysteme (percent disconnected fiber map).


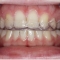
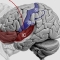
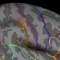
Zeitliche Folge des Schluckens eines Bolus (grün eingefärbt) und der sequentiellen Aktivierung des Gehirns.
Diese Studie wurde von der DFG gefördert (LO 795/12-1 und 12-2).
Publikationen:
Domin M., Mihai G.P., Platz T., Lotze M. (2022) Swallowing function in the chronic stage following stroke is associated with white matter integrity of the callosal tract between the interhemispheric S1 swallowing representation areas. Neuroimage Clinical, 35 (2022) 103093
Mihai, P.G., Otto, M., Domin, M., Platz, T., Hamdy, S., Lotze, M. (2016) Brain imaging correlates of recovered swallowing after dysphagic stroke: an fMRI and DWI study. Neuroimage Clinical, 2:1013-1021.
Windel AS*, Mihai PG*, Lotze M. (2015) Neuroimaging of swallowing in the elderly, Behavioral Brain Research, 286:308-17.
Mihai P.G., Otto M., Platz T., Eickhoff S.B., Lotze M. (2014) Sequential evolution of cortical activity and effective connectivity of swallowing using fMRI. Human Brain Mapping,35(12): 5962-73.
Mihai PG, von Bohlen und Halbach O, Lotze M (2013) Differentiation of cerebral representation of occlusion and swallowing with fMRI. Am J Physiol.304(10):G847-54.
Lotze M., Mihai G.P., Seggewies G. (2013) Darstellung der zerebralen Steuerung des Schluckens. Neuroreha, 4: 154-159.
Lotze M., Seggewies G., Erb M., Grodd W., Birbaumer N. (2000) The representation of articulation in the primary sensorimotor cortex. NeuroReport 11: 2985-2989.